Diabetic Assessment
Diabetes is a global public health problem which carries significant health problems. Wakefield Podiatrists recommend diabetics should have annual foot health checks.The examination takes approximately 60 minutes and produces a comprehensive picture of your foot health. Our assessments are far more comprehensive than the simple tests performed at your local GP's. Regular assessments provide an accurate picture of how your feet are coping with diabetes and enables us to provide bespoke education and treatment for your feet. Assessment includes :-
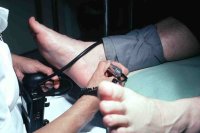
Blood pressure assessment Blood pressure of the heart and feet, full Doppler assessment.
Nerve assessment Clinical tests, nerve conduction studies if needed.
Infection risk assessment Visual inspection of the feet, culture and microscopy if needed.
Chiropody care advice Advice on nail care and hard skin management.
Insole assessment Static and weight bearing measurement of plantar pressures, provide insoles if needed.
Footwear advice Advice on footwear to try and prevent ulceration.
Surgical intervention Referral to a consultant foot surgeon for where ulcer management, nerve decompression.
Nail care and hard skin
The importance of nail care and hard skin reduction cannot be underestimated. The Podiatrist will cut nails and remove hard skin whilst being able to assess the foot for infection.
Fungal Infection
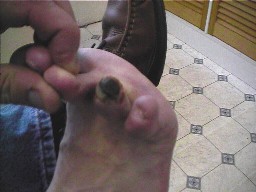
Diabetics are significantly more likely to suffer from fungal infections and sometimes the only clue an individual may have diabetes is regular bouts of fungal infection. Fungal infection usually occurs in the toe nails as Onychomycosis or on the skin as Athlete's foot. It is the Podiatrists role to diagnose fungal infection and eradicate whenever possible. Treatment is based around the Podiatrist prescribing topical and oral anti-fungal drugs to eradicate the infection, patient education and regular visits to the Podiatrist for nail care and skin checks.
Vascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease is a serious, long-term complication of diabetes. Uncontrolled blood sugars and fats damage blood vessels throughout the body leaving the individual susceptible to strokes, heart attacks, amputations, infections, loss of sight and decreased life expectancy. Management is based around controlling blood sugar levels,eating properly, exercising, stopping drinking and smoking, dieting and taking medications. It is the Podiatrists job to assess a diabetic’s pulses, blood pressure and that the skin is assessed for changes and to ensure that the foot has a healthy blood supply. A special instrument called a Doppler enables a Podiatrist to listen to the pulses within the feet and a Podiatrist will use an inflatable cuff around the ankle and take the blood pressure; this procedure will also be carried out with the arm. A special value will be calculated called the Ankle Brachial Pressure Index, this value enables a Podiatrist to gauge how healthy diabetics arteries and blood supply are within the foot.
Nerve Damage
High blood sugar levels can damage nerves. Unfortunately nothing can rejuvenate or replace nerves that have been damaged or have died because of diabetes. The damage to a diabetics nerves is called Neuropathy and is a major factor in ulcer development and amputation from infection. . Neuropathy can also be extremely painful and can lead to loss of sensation in the feet, and dysfunction to other areas of the body. Medications may be prescribed to help with Neuropathy. A Podiatrist will perform several clinical tests to assess for neuropathy and may organise a nerve conduction test if uncertain of diagnosis
Ulcers & Amputations
Ulcers can form from poor circulation of the arteries, poor drainage from the veins or from infection to a open wound. Ulcers can go undetected due to the diabetic not being able to see the ulcer due to poor eye sight, compromised mobility, or an inability to feel pain from Neuropathy. Poor blood flow into the foot coupled with an increased risk of infection and a compromised immune system creates a perfect storm of variables leading to ulcer formation which may ultimately lead to amputation due to the antibiotic resistant infection. Treatment will depend on the ulcer type. Medication and meticulous wound care may heal the ulcer, sometimes surgery is indicated. Ulcers and amputations can be avoided with regular foot health checks and also measuring pressure on the underside of a diabetics foot these are known as plantar pressures and can be useful in diagnosing hot spots for ulcer formation. Regular visits to your Podiatrist alongside a annual diabetic foot health assessment will minimise your chances of developing these problems. Good shoes and meticulous inspection of the feet and toenails on a daily basis (with a good light and mirror if necessary) can detect the earliest signs and is one of the best A Podiatrist may measure the pressures in on the underside of a foot and prescribe special insoles designed to reduce thesepressures and potential ulcers.
Please call us if you would like to discuss your diabetic treatment.